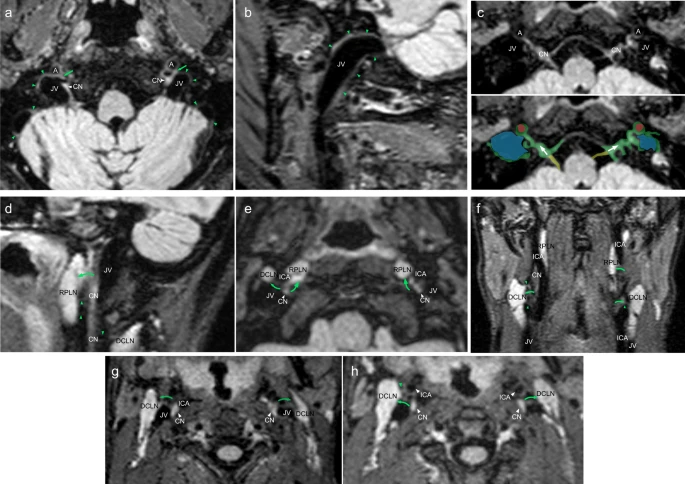
El índice anchura del asta frontal respecto a la distancia intercaudados decrece. Lo normal es entre 2.2 y 2.6.
Neuroimagen.com
Un blog con contenidos visuales de neuroimagen
sábado, 30 de julio de 2022
martes, 18 de enero de 2022
sábado, 21 de agosto de 2021
jueves, 1 de abril de 2021
martes, 12 de marzo de 2019
jueves, 21 de abril de 2016
Signo de la golondrina en la Enfermedad de Parkinson
Axial SWI Clinical high resolution 3D-T2*/SWI MRI (Philips ‘PRESTO’ sequence) of a Parkinson's disease patient showing absence of the normal high SWI signal within the nigrosome-1 bilaterally (absent swallow tail sign). Image and text used under creative commons licence CC BY 3.0. Original source: Schwarz ST, Afzal M, Morgan PS et-al. The 'swallow tail' appearance of the healthy nigrosome - a new accurate test of Parkinson's disease: a case-control and retrospective cross-sectional MRI study at 3T. PLoS ONE. 2014;9 (4): e93814. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0093814 Clinical high resolution 3D-T2*/SWI MRI (Philips ‘PRESTO’ sequence) of a Parkinson's disease patient showing absence of the normal high SWI signal within the nigrosome-1 bilaterally (absent swallow tail sign). Image and text used under creative commons licence. Original source: Schwarz ST, Afzal M, Morgan PS et-al. The 'swallow tail' appearance of the healthy nigrosome - a new accurate test of Parkinson's disease: a case-control and retrospective cross-sectional MRI study at 3T. PLoS ONE. 2014;9 (4): e93814. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0093814
Texto completo
Abducens nerve on MRI
Annotated MRI (FIESTA)
Modality: MRI

MRI Axial T2 FIESTA
Annotated high resolution FIESTA sequence through the medulla and pons demonstrates the normal course of the abducens nerve (CN VI) (white arrow) as it ascends from the ponto-medullary junction to Dorello's canal.
Modality: MRI

MRI Axial T2 FIESTA
Annotated high resolution FIESTA sequence through the medulla and pons demonstrates the normal course of the abducens nerve (CN VI) (white arrow) as it ascends from the ponto-medullary junction to Dorello's canal.
sábado, 7 de noviembre de 2015
Resonancia de 7T para detectar Enfermedad de Alzheimer
domingo, 17 de mayo de 2015
Midiendo el volumen del bulbo olfatorio como método diagnóstico para la Enfermedad de Parkinson
 |
| A. Paciente con Atrofia Multisistema, presenta una morfología del bulbo olfatorio normal. B. Paciente con Parkinson, con reducción del volumen del bulbo. |
DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.parkreldis.2015.05.001
Suscribirse a:
Comentarios (Atom)